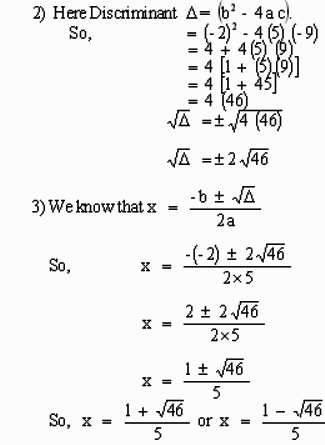Now we will see a few quadratic equations using the formula method.
a) Solve the quadratic equation 5 x 2 - 2 x - 9 = 0.
Solution:
1) Comparing 5 x 2 - 2 x - 9 = 0 with a x 2 + b x + c = 0 we get,
a = 5, b = - 2, c = - 9
b) Solve the quadratic equation 3 x 2 - 4 x - 3 = 0.
Solution:
1) Comparing 3 x 2 - 4 x - 3 = 0 with a x 2 + b x + c = 0 we get,
a = 3, b = - 4, c = - 3
Now we will see some rules about the roots of the quadratic equation.
1) Sum of the roots (α, β) of the quadratic equation a x 2 + b x + c = 0,
α + β = - b / a and α β = c / a
α + β = - Coefficient of x / Coefficient of x 2 and α β = Constant / Coefficient of x 2.
2) If α and β are the roots of the quadratic equation then the quadratic equation will be
x 2 - (Sum of the roots) x + (Product of the roots) = 0,
x 2 - (α + β) x + (α β) = 0,
Now we will see some important problems in Quadratic equations and the roots of the Quadratic Equations
a) If the sum of the roots of the quadratic equation is 3 and the sum of their cubes is 63, then find the equation.
Solution:
1) Here, α + β = 3 and α 3 + β 3 = 63
2) We know that , α 3 + β 3 = (α + β)3 - 3 α β (α + β)
so , 63 = (3)3 - 3 α β (3)
63 = 27 - 9 α β Dividing by 9 through out we get
7 = 3 - α β
α β = 3 - 7
α β = - 4
3) We know that the quadratic equation will be
x 2 - (α + β) x + (α β) = 0
x 2 - (3) x + (- 4) = 0
x 2 - 3 x - 4 = 0
4) Answer: So the required quadratic equation will be x 2 - 3 x - 4 = 0.
A few more problems on Quadratic Equations related to factors will be discussed in the next Blog.